 |
| Causes of Yellow Fever and How We Can Prevent It |
What is
it?
Yellow fever, also known as Siam disease or
Barbados fever, is a rapidly evolving, acute infectious disease transmitted by
the bite of the mosquito. The severity can be very variable; Regardless of its
intensity, once suffered, the patient acquires lifelong immunity. It generally
manifests itself in high-mortality outbreaks in the African, Central and South
American regions.
The number of people infected with this
disease has increased in the last two decades due to a decrease in the immunity
of the population, deforestation, population movements, climate change and
urbanization. For a Vaccine for yellow fever, visit Travel Clinic in Bexley.
Causes
Yellow fever is caused by a virus that is
transmitted by the bite of mosquitoes. A person can become infected if the
mosquito is infected with the virus.
Despite being a disease that is localized in
specific countries of the world (especially in South America and sub-Saharan
Africa), anyone can be infected, although older people have a higher risk of
reaching the severe stage of the disease.
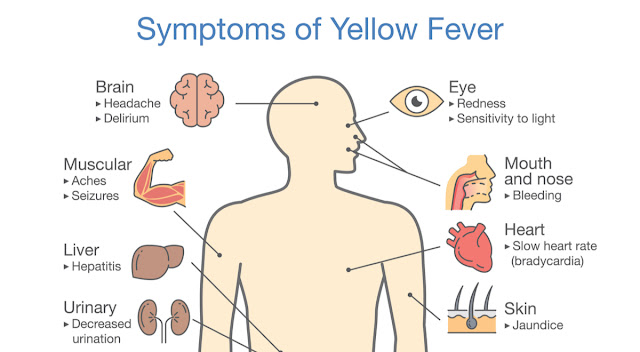
Symptoms.
Once the virus is contracted and after an
incubation period of 3 to 6 days, the infection can develop in one or two
phases, depending on how the disease evolves:
The first stage or acute phase: In this first
period, the most common symptoms are fever, myalgia with severe back pain,
chills, headaches, nausea or vomiting and loss of appetite. Later, most
patients improve and symptoms resolve within 3 to 4 days. The second stage or
toxic phase: 15 per cent of patients reach this state. In this case, the fever becomes
higher and different organ systems are affected.
Afterwards, the patient becomes jaundiced and
complains of abdominal pain with vomiting. In addition, oral, nasal, eye or
gastric bleeding, blood in vomit or stool, and kidney failure may occur. Half of
the patients who enter this phase die within 10 to 14 days and the rest recover
without serious damage to their organs.
Prevention
Vaccination is the most effective measure
against contagion, which is why the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends
it for any trip outside urban areas in countries located in areas of Central
and South America and part of Sub-Saharan Africa. This vaccine must be
administered in official vaccination centres accredited by WHO.
One dose provides immunity for ten years from the tenth day of administration.
It causes adverse effects, such as local pain, muscle aches or headaches, and
fever may also appear. It is contraindicated during pregnancy, in people
allergic to eggs, in immunosuppressed patients and in children under nine
months of age.
Other prevention measures are avoiding
mosquito bites and controlling their reproduction.
Types
Those most affected by yellow fever are humans
and monkeys. Its transmission can occur from one animal to another or by the
bite of a mosquito. It can be classified into three types according to its
three different forms of transmission.
Jungle: It occurs in tropical forests. It is
caused by the bite of a carrier mosquito. It is usually rare but affects mainly
monkeys, which in turn can infect other mosquitoes that feed on their blood and
these to people who enter the jungle.
Intermediate: Typical of the humidor
semi-humid savannas of Africa. It produces several cases simultaneously and in
separate populations. It causes few deaths, but if left unchecked, it can
generate the most serious urban yellow fever epidemic.
Urban or epidemic: The Aedes aegypti mosquito
acts as a transmitting agent between people in areas of high population
density, being able to generate large epidemics where the virus is transmitted
from one person to another with great ease.
I demand dress missed something, however there are a numerous of pairs in this cool who could spry graded the carriers. iron test clinic malaysia
ReplyDelete